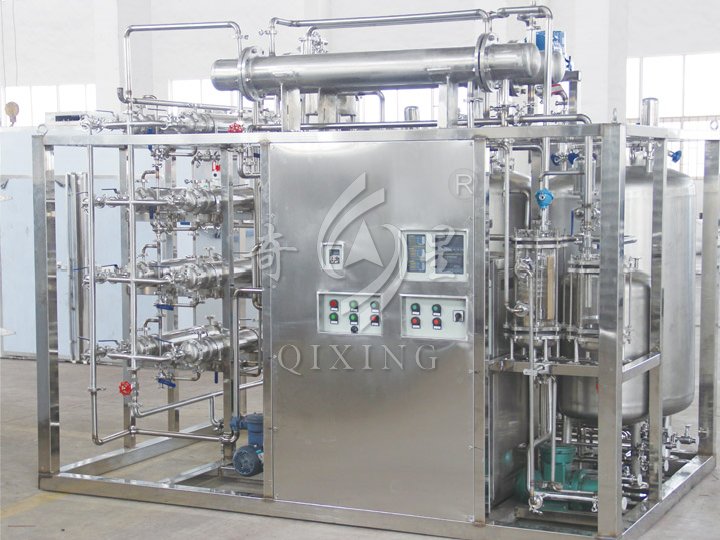
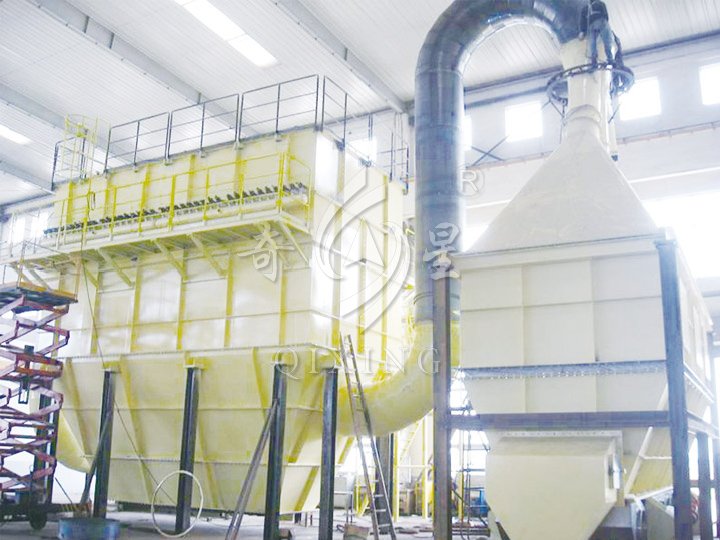
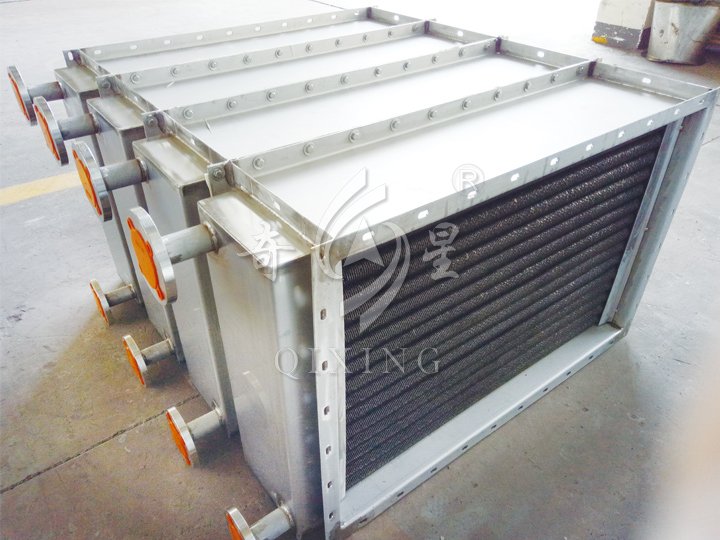
Spray Drying Equipment for Molecular Sieves
Tags:
Class: Spray Dryer Production Line
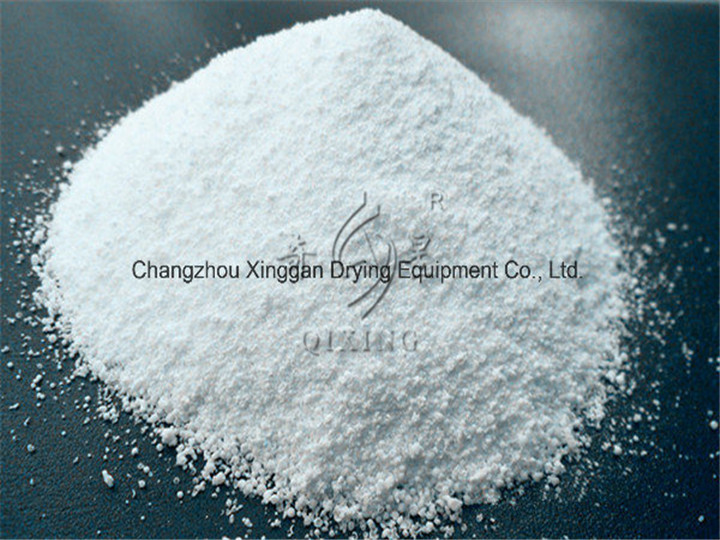
Overview: A molecular sieve is a material with pores (very small holes) of uniform size. These pore diameters are similar in size to small molecules, and thus large molecules cannot enter or be absorbed, while smaller molecules can.
Detail Images
INTRODUCTION
A molecular sieve is a material with pores (very small holes) of uniform size. These pore diameters are similar in size to small molecules, and thus large molecules cannot enter or be absorbed, while smaller molecules can. As a mixture of molecules migrate through the stationary bed of porous, semi-solid substance referred to as a sieve (or matrix), the components of highest molecular weight (which are unable to pass into the molecular pores) leave the bed first, followed by successively smaller molecules. Some molecular sieves are used in chromatography, a separation technique that sorts molecules based on their size. Other molecular sieves are used as desiccants (some examples include activated charcoal and silica gel).
The diameter of a molecular sieve is measured in ångströms (Å) or nanometres (nm). According to IUPAC notation, microporous materials have pore diameters of less than 2 nm (20 Å) and macroporous materials have pore diameters of greater than 50 nm (500 Å); the mesoporous category thus lies in the middle with pore diameters between 2 and 50 nm (20-500 Å).
APPLICATION
Molecular sieves are often utilized in the petroleum industry, especially for drying gas streams. For example, in the liquid natural gas (LNG) industry, the water content of the gas needs to be reduced to less than 1 ppmv to prevent blockages caused by ice.
In the laboratory, molecular sieves are used to dry solvent. "Sieves" have proven to be superior to traditional drying techniques, which often employ aggressive desiccants.
Under the term zeolites, molecular sieves are used for a wide range of catalytic applications. They catalyze isomerisation, alkylation, and epoxidation, and are used in large scale industrial processes, including hydrocracking and fluid catalytic cracking.
They are also used in the filtration of air supplies for breathing apparatus, for example those used by scuba divers and firefighters. In such applications, air is supplied by an air compressor and is passed through a cartridge filter which, depending on the application, is filled with molecular sieve and/or activated carbon, finally being used to charge breathing air tanks. Such filtration can remove particulates and compressor exhaust products from the breathing air supply.
A molecular sieve is a material with pores (very small holes) of uniform size. These pore diameters are similar in size to small molecules, and thus large molecules cannot enter or be absorbed, while smaller molecules can. As a mixture of molecules migrate through the stationary bed of porous, semi-solid substance referred to as a sieve (or matrix), the components of highest molecular weight (which are unable to pass into the molecular pores) leave the bed first, followed by successively smaller molecules. Some molecular sieves are used in chromatography, a separation technique that sorts molecules based on their size. Other molecular sieves are used as desiccants (some examples include activated charcoal and silica gel).
The diameter of a molecular sieve is measured in ångströms (Å) or nanometres (nm). According to IUPAC notation, microporous materials have pore diameters of less than 2 nm (20 Å) and macroporous materials have pore diameters of greater than 50 nm (500 Å); the mesoporous category thus lies in the middle with pore diameters between 2 and 50 nm (20-500 Å).
APPLICATION
Molecular sieves are often utilized in the petroleum industry, especially for drying gas streams. For example, in the liquid natural gas (LNG) industry, the water content of the gas needs to be reduced to less than 1 ppmv to prevent blockages caused by ice.
In the laboratory, molecular sieves are used to dry solvent. "Sieves" have proven to be superior to traditional drying techniques, which often employ aggressive desiccants.
Under the term zeolites, molecular sieves are used for a wide range of catalytic applications. They catalyze isomerisation, alkylation, and epoxidation, and are used in large scale industrial processes, including hydrocracking and fluid catalytic cracking.
They are also used in the filtration of air supplies for breathing apparatus, for example those used by scuba divers and firefighters. In such applications, air is supplied by an air compressor and is passed through a cartridge filter which, depending on the application, is filled with molecular sieve and/or activated carbon, finally being used to charge breathing air tanks. Such filtration can remove particulates and compressor exhaust products from the breathing air supply.
News
- 2018-05-11 > Tow CT-C Hot Air Circulation Ovens Manufactured by Our Company Were Exported to Bangladesh
- 2018-04-25 > 2018 (Spring) China International Pharmaceutical Machinery Exposition
- 2018-02-23 > New Year Begins a New Journey
- 2017-10-04 > 2017(Autumn) Professional Pharmaceutical Machinery Exhibition in China
- 2017-06-24 > Xinggan Drying Successfully Participated in the 17th Pharmaceutical Raw Materials Exhibition
- 2017-04-22 > 2017(Spring) Professional Pharmaceutical Machinery Exhibition in Qingdao
Products